Warts are nothing more than a skin pathology that is not inflammatory in nature. The disease manifests itself in the form of benign neoplasms in the epidermis, the size of which can reach 10-15 mm. Neoplasms of this type do not have favorite places of localization, first a wart may appear on the finger, and then on the face and legs. The unsightly appearance of warts is the main reason why many women, as well as men, prefer to get rid of unwanted skin growths.
Clinical picture and characteristics of the disease

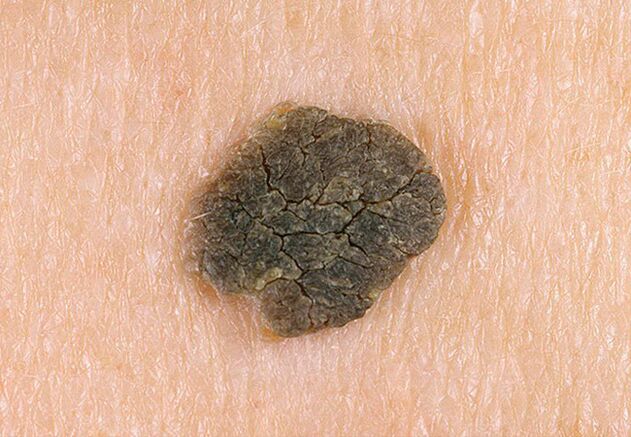
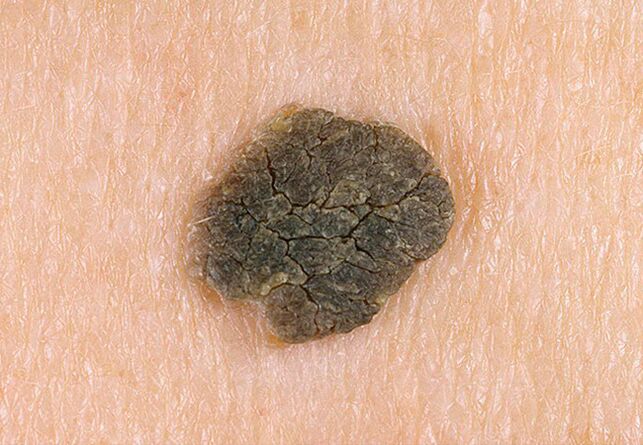
Warts are called rounded formations that occur on the surface of the skin as a result of overgrowth of the upper layer of the epithelium, as well as the subcutaneous papillary ball located directly below it. Sometimes the appearance of formations is not related to the proliferation of the epithelium, as they can appear due to infection of the skin by the human papillomavirus (HPV). In any case, warts on the soles, hands and also on the face bring a lot of inconvenience, even the development of psychological complexes, which is why the problem of dealing with them is quite relevant.
The size of the papule depends on its location and variety. The minimum size of the formation is 1. 5 mm, the maximum is 6 cm.
Observation! Warts tend to combine, which causes the size of the papules to increase significantly. The neoplasm assumes a cylindrical or hemispherical shape, has a rather bulky appearance and causes disorders of a psychological and physical nature.
In the early stages of development, the color of the papule does not differ from the color of the skin, however, after a certain time, the formation becomes purple and sometimes even black. Partly due to this color, warts are due to dirt, which adheres perfectly to the rough surface of the formation. The change in color characteristics occurs many times faster if the warts are located on the legs.
What is the reason for the appearance of warts, the etiology of their formation?
When warts appear, the cause of development is the penetration of human papillomavirus infection into the human body.
Additional information! A person can be a carrier of the virus for a long time, but due to the absence of manifestations of pathology in the form of warts, do not even guess.
Methods of infection with the virus:
- the presence of wounds and micro-cracks on the skin contributes to the penetration of the virus inside;
- during close contact with an affected patient. Thus, most of the time the disease is transmitted sexually;
- the use of hygiene products and things of the affected person can also lead to infection with the virus;
- you can catch the papillomavirus infection in places of public use, such as gym, swimming pool, spa, sauna;
- if the mother is a carrier of the virus, it can be transmitted to the child as it passes through the birth canal.
Important! To prevent the infection of the baby with the papillomavirus, special attention should be paid to the treatment of the pathology during pregnancy.
Factors that contribute to the development of the disease:
- leading a hectic lifestyle, frequent change of sexual partners;
- negligence of hygiene rules;
- weakened immunity. Even if a person is a carrier of the virus, strong immunity will not allow it to become active;
- frequent stress;
- transferred infectious disease;
- chronic fatigue;
- hormonal imbalance;
- avitaminosis;
- precarious environmental situation;
- work involving the use of aggressive materials.
types of warts
Depending on the characteristics of warts and the symptoms that accompany their occurrence, there are four main types of neoplasms.
So, the types of warts:
- ordinary or simple;
- apartment;
- senile;
- pointed condyloma.
Let's dwell in more detail on the characteristics and characteristics of each type.
Features of a simple wart
Features of a common wart (common warts) include:
- the predominant location is the back of the hand;
- papule diameter from 1 to 10 mm;
- Common warts usually go away on their own within two years and do not require special treatment.
A variety of simple warts is plantar (plantar warts).
Features of plantar warts:
- leg warts are more likely to appear in people characterized by excessive leg sweating;
- papules are located mainly in places of greater pressure of shoes on the skin;
- at first, the papule has a yellowish-gray tinge, a rough, uneven surface. Advanced stages of the pathology are characterized by a change in color to dirty gray, a significant compaction of the affected covering, its keratinization;
- leg warts are among the most painful. In some cases, the development of the disease leads to partial disability;
- as a rule, warts on the legs look unique, but sometimes their number reaches 5-6. As the disease develops, small plaques may fuse together, forming a mosaic wart.
flat wart or juvenile wart
The main difference between flat and juvenile formations (flat warts) is the fact that these warts appear more often in children and teenagers.
Flat warts signs:
- smooth surface of the papule, the size in diameter does not exceed 1. 5 mm;
- the height of the elevation above the areas close to the epidermis reaches 2 mm;
- the shape is round or irregular;
- localization places - the outer surface of the hands, the skin of the face, the lower part of the legs;
- the papule does not stand out strongly on the surface of the skin, due not only to its flat shape, but also to its light color (pink, flesh);
- The etiology of juvenile warts is associated with exposure to external stimuli. Thus, the formation may appear at the site of a cut or injury to the skin.
Symptoms and Characteristics of a Pointed Wart
Signs that characterize this type of wart, such as condyloma (genital warts), include:
- pink growths that occur in the early stages of the development of the pathology gradually merge, forming a type of growth located on a base that looks like a leg;
- a favorite place for the location of warts of this type is the genitals, both female and male;
- condyloma is transmitted by contact. The risk of contracting a disease increases if there are micro-cracks and sores on the carrier's genitals;
- a pointed wart is characterized by growth, so when the first signs of a disease are found, you should immediately contact a dermatologist;
- condyloma is a very fertile ground for the manifestation and development of other pathologies of the inguinal zone. Thus, the lack of treatment in women can lead to the development of a disease as serious as cervical cancer.
Signs of seborrheic keratosis
Senile wart or the so-called seborrheic keratosis: signs and characteristics of education:
- characteristic of elderly people;
- presumably, the cause of the development of the pathology is the defeat of the cells of the main layer of the skin;
- this type of wart has nothing to do with HPV;
- most often, manifestations of the disease affect the skin of the chest, less often - face, neck, hands, forearms and legs;
- the multiple nature of the formations, usually the number of keratosis elements does not exceed 20;
- the predisposition to seborrheic warts is genetically transmitted;
- the minimum papule size in diameter is 2 mm, the maximum is 6 cm.
The clinic of senile wart depends on the stage of its development and location on the body. In the early stages, they are flat spots with well-defined edges, pink or yellow, covered with easily scaly crusts. Over time, the crusts thicken, their thickness reaches two cm. With the development of pathology, papules take the form of a fungus, become dark brown or even black.
The process of developing a seborrheic wart takes more than a dozen years, but no malignant transformation occurs with papules during this period.
Features of wart treatment
What you need to know when treating warts:
- it is completely impossible to get rid of the papillomavirus infection, it will remain in the body forever. The main task of the carrier is to deactivate the virus, transfer it to a latent form;
- the disease is recurrent;
- after removing the wart on the epidermis, as a rule, marks remain in the form of scars and scars;
- formations sometimes disappear on their own, especially for young patients.
Important! The identification of the first signs of warts should not cause panic, a timely visit to a dermatologist and the appointment of an effective treatment will help to get rid of the signs of pathology and maximize the period of remission.
Traditional methods of dealing with warts
Observation! The therapeutic course is based on the use of drugs and classical techniques, however, in the early stages of the disease, clear success can be achieved with the help of traditional medicine.
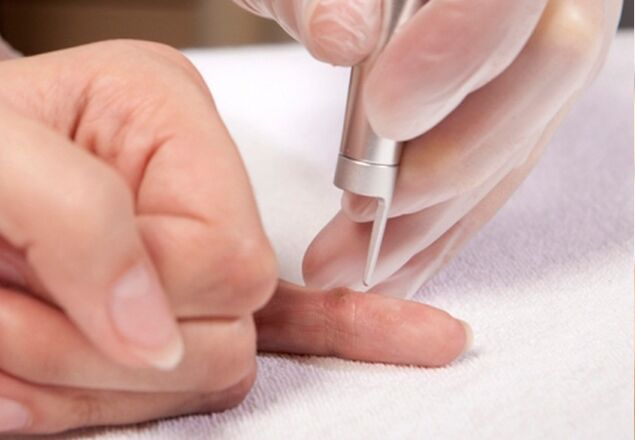
Comprehensive treatment of warts involves the use of general and local medications, as well as medical procedures.
Popular methods of dealing with warts:
- laser papule removal. It is considered one of the most effective and quick methods, it does not harm the skin;
- electrocoagulative method. Promotes growth reduction by exposure to high temperatures;
- cryotherapy or cautery;
- surgical removal. This method is used very rarely.
Is it possible to get rid of warts with traditional medicine?
The following folk remedies have a beneficial effect in the treatment of neoplasms:
- celandine juice. Used to cauterize papules;
- celandine-based compresses and decoctions;
- dandelion juice rubbing. Lubricate the affected areas should be at least three times a day;
- garlic and onion juice;
- healing infusion based on wormwood.
You can get rid of warts by performing cold procedures. Cauterization with vinegar gives a positive effect. However, when using vinegar or its essence, safety rules must be followed.
The appearance of a wart on the skin indicates disorders in the body; therefore, when the first signs of pathology are detected, it is recommended to consult a doctor to diagnose the disease and prescribe treatment.


















